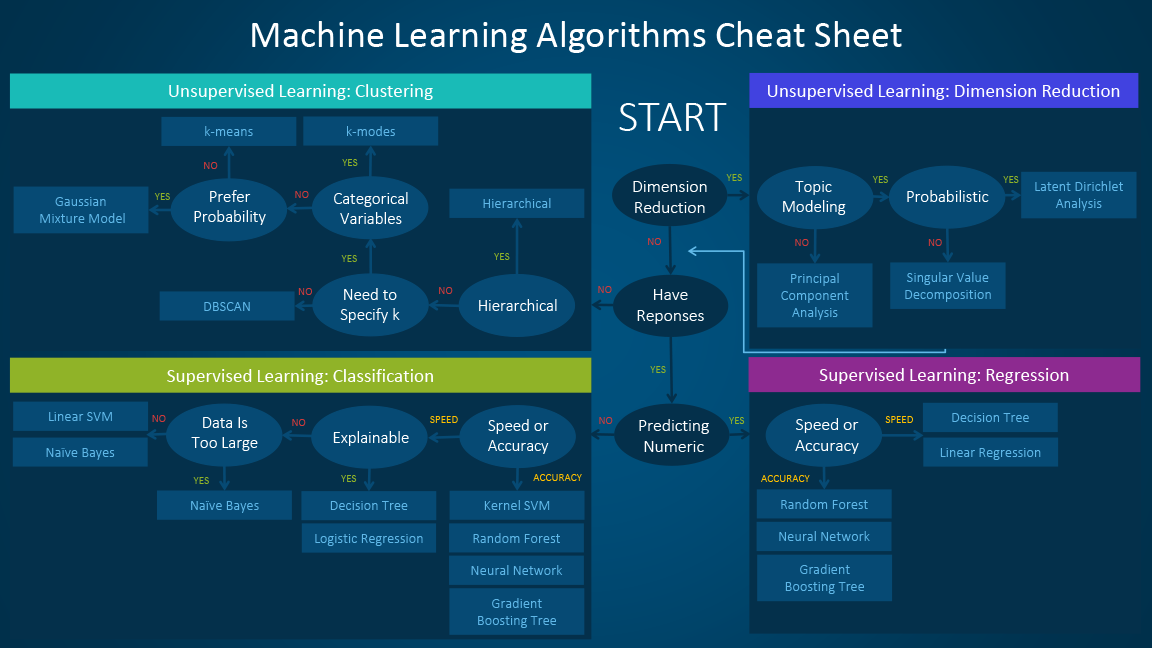
Machine Learning Cheatsheets. In Data Science, by using machine learning you can perform fraud and risk detection, Spam filtering, Face and Voice Recognition, etc. So if you are focusing on machine learning, then these machine learning cheat sheets will be essential for you-Machine Learning Formulas; Machine Learning Algorithm Cheat Sheet. This cheat sheet is designed to give you ideas to lift performance on your machine learning problem. All it takes is one good idea to get a breakthrough. Find that one idea, then come back and find another. I have divided the list into 4 sub-topics: Improve Performance With Data. Improve Performance With Algorithms.
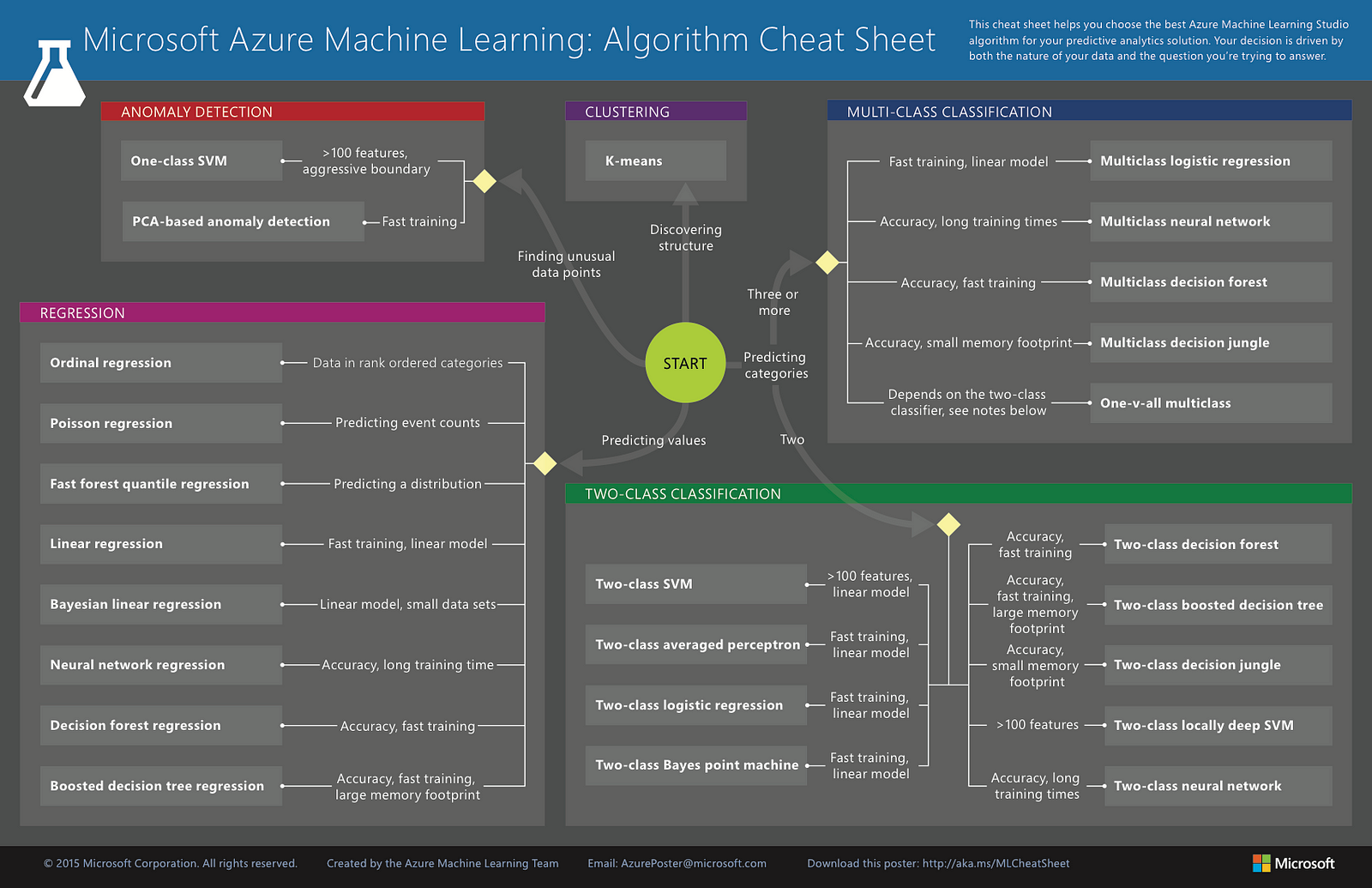
Python For Data Science Cheat Sheet Python Basics Variables and Data T string es at Select t Jupyter spyder Lists ecu ANACONDA 20 Nu mpy np G. Ther Microsoft Azure Machine Learning: Algorithm Cheat Sheet CLUSTERING START TWO-CLASS CLASSIFICATION training. Gear up to speed and have concepts and commands handy in Data Science, Data Mining, and Machine learning algorithms with these cheat sheets covering R, Python, Django, MySQL, SQL, Hadoop, Apache Spark, Matlab, and Java. Machine Learning tips and tricks cheatsheet Star. By Afshine Amidi and Shervine Amidi. Classification metrics. In a context of a binary classification, here are the.
By Afshine Amidi and Shervine Amidi
Classification metrics
In a context of a binary classification, here are the main metrics that are important to track in order to assess the performance of the model.
Confusion matrix Gazette garage sales. The confusion matrix is used to have a more complete picture when assessing the performance of a model. It is defined as follows:
| Predicted class | |||
| + | - | ||
| Actual class | + | TP True Positives | FN False Negatives Type II error |
| - | FP False Positives Type I error | TN True Negatives |
Main metrics The following metrics are commonly used to assess the performance of classification models:
| Metric | Formula | Interpretation |
| Accuracy | $displaystylefrac{textrm{TP}+textrm{TN}}{textrm{TP}+textrm{TN}+textrm{FP}+textrm{FN}}$ | Overall performance of model |
| Precision | $displaystylefrac{textrm{TP}}{textrm{TP}+textrm{FP}}$ | How accurate the positive predictions are |
| Recall Sensitivity | $displaystylefrac{textrm{TP}}{textrm{TP}+textrm{FN}}$ | Coverage of actual positive sample |
| Specificity | $displaystylefrac{textrm{TN}}{textrm{TN}+textrm{FP}}$ | Coverage of actual negative sample |
| F1 score | $displaystylefrac{2textrm{TP}}{2textrm{TP}+textrm{FP}+textrm{FN}}$ | Hybrid metric useful for unbalanced classes |
ROC The receiver operating curve, also noted ROC, is the plot of TPR versus FPR by varying the threshold. These metrics are are summed up in the table below:
| Metric | Formula | Equivalent |
| True Positive Rate TPR | $displaystylefrac{textrm{TP}}{textrm{TP}+textrm{FN}}$ | Recall, sensitivity |
| False Positive Rate FPR | $displaystylefrac{textrm{FP}}{textrm{TN}+textrm{FP}}$ | 1-specificity |
AUC The area under the receiving operating curve, also noted AUC or AUROC, is the area below the ROC as shown in the following figure:
Regression metrics
Basic metrics Given a regression model $f$, the following metrics are commonly used to assess the performance of the model:
| Total sum of squares | Explained sum of squares | Residual sum of squares |
| $displaystyletextrm{SS}_{textrm{tot}}=sum_{i=1}^m(y_i-overline{y})^2$ | $displaystyletextrm{SS}_{textrm{reg}}=sum_{i=1}^m(f(x_i)-overline{y})^2$ | $displaystyletextrm{SS}_{textrm{res}}=sum_{i=1}^m(y_i-f(x_i))^2$ |
Coefficient of determination The coefficient of determination, often noted $R^2$ or $r^2$, provides a measure of how well the observed outcomes are replicated by the model and is defined as follows:
[boxed{R^2=1-frac{textrm{SS}_textrm{res}}{textrm{SS}_textrm{tot}}}]Main metrics The following metrics are commonly used to assess the performance of regression models, by taking into account the number of variables $n$ that they take into consideration:
| Mallow's Cp | AIC | BIC | Adjusted $R^2$ |
| $displaystylefrac{textrm{SS}_{textrm{res}}+2(n+1)widehat{sigma}^2}{m}$ | $displaystyle2Big[(n+2)-log(L)Big]$ | $displaystylelog(m)(n+2)-2log(L)$ | $displaystyle1-frac{(1-R^2)(m-1)}{m-n-1}$ |
where $L$ is the likelihood and $widehat{sigma}^2$ is an estimate of the variance associated with each response.
Model selection
Vocabulary When selecting a model, we distinguish 3 different parts of the data that we have as follows:
| Training set | Validation set | Testing set |
| • Model is trained • Usually 80% of the dataset | • Model is assessed • Usually 20% of the dataset • Also called hold-out or development set | • Model gives predictions • Unseen data |
Once the model has been chosen, it is trained on the entire dataset and tested on the unseen test set. These are represented in the figure below:
Cross-validation Cross-validation, also noted CV, is a method that is used to select a model that does not rely too much on the initial training set. The different types are summed up in the table below:
| k-fold | Leave-p-out |
| • Training on $k-1$ folds and assessment on the remaining one • Generally $k=5$ or $10$ | • Training on $n-p$ observations and assessment on the $p$ remaining ones • Case $p=1$ is called leave-one-out |
The most commonly used method is called $k$-fold cross-validation and splits the training data into $k$ folds to validate the model on one fold while training the model on the $k-1$ other folds, all of this $k$ times. The error is then averaged over the $k$ folds and is named cross-validation error.
Regularization The regularization procedure aims at avoiding the model to overfit the data and thus deals with high variance issues. The following table sums up the different types of commonly used regularization techniques:
| LASSO | Ridge | Elastic Net |
| • Shrinks coefficients to 0 • Good for variable selection | Makes coefficients smaller | Tradeoff between variable selection and small coefficients |
| $..+lambda||theta||_1$ $lambdainmathbb{R}$ | $..+lambda||theta||_2^2$ $lambdainmathbb{R}$ | $..+lambdaBig[(1-alpha)||theta||_1+alpha||theta||_2^2Big]$ $lambdainmathbb{R},alphain[0,1]$ |
Diagnostics
Bias The bias of a model is the difference between the expected prediction and the correct model that we try to predict for given data points.
Variance The variance of a model is the variability of the model prediction for given data points.
Bias/variance tradeoff The simpler the model, the higher the bias, and the more complex the model, the higher the variance.
| Underfitting | Just right | Overfitting | |
| Symptoms | • High training error • Training error close to test error • High bias | • Training error slightly lower than test error | • Very low training error • Training error much lower than test error • High variance |
| Regression illustration | |||
| Classification illustration | |||
| Deep learning illustration | |||
| Possible remedies | • Complexify model • Add more features • Train longer | • Perform regularization • Get more data |
Error analysis Error analysis is analyzing the root cause of the difference in performance between the current and the perfect models.
Ablative analysis Ablative analysis is analyzing the root cause of the difference in performance between the current and the baseline models.
© TechRepublic Machine learning: A cheat sheet
Artificial intelligence (AI), which has been around since the 1950s, has seen ebbs and flows in popularity over the last 60+ years. But today, with the recent explosion of big data, high-powered parallel processing, and advanced neural algorithms, we are seeing a renaissance in AI--and companies from Amazon to Facebook to Google are scrambling to take the lead. According to AI expert Roman Yampolskiy, 2016 was the year of 'AI on steroids,' and its explosive growth hasn't stopped.
While there are different forms of AI, machine learning (ML) represents today's most widely valued mechanism for reaching intelligence. Here's what it means.
SEE: Managing AI and ML in the enterprise (ZDNet special report) | Download the report as a PDF (TechRepublic)
Executive summary
- What is machine learning? Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence. Instead of relying on explicit programming, it is a system through which computers use a massive set of data and apply algorithms to 'train' on--to teach themselves--and make predictions.
- When did machine learning become popular? The term 'artificial intelligence' was coined in the 1950s by Alan Turing. Machine learning became popular in the 1990s, and returned to the public eye when Google's DeepMind beat the world champion of Go in 2016. Since then, ML applications and machine learning's popularity have only increased.
- Why does machine learning matter? Machine learning systems are able to quickly apply knowledge and training from large data sets to excel at facial recognition, speech recognition, object recognition, translation, and many other tasks.
- Which industries use machine learning? Machine learning touches industries spanning from government to education to healthcare. It can be used by businesses focused on marketing, social media, customer service, driverless cars, and many more. It is now widely regarded as a core tool for decision making.
- How do businesses use machine learning? Business applications of machine learning are numerous, but all boil down to one type of use: Processing, sorting, and finding patterns in huge amounts of data that would be impractical for humans to make sense of.
- What are the security and ethical concerns about machine learning? AI has already been trained to bypass advanced antimalware software, and it has the potential to be a huge security risk in the future. Ethical concerns also abound, especially in relation to the loss of jobs and the practicality of allowing machines to make moral decisions like those that would be necessary in self-driving vehicles.
- What machine learning tools are available? Businesses like IBM, Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and others offer tools for machine learning. There are free platforms as well.
SEE: Managing AI and ML in the enterprise 2020: Tech leaders increase project development and implementation (TechRepublic Premium)
What is machine learning?
Machine learning is a branch of AI. Other tools for reaching AI include rule-based engines, evolutionary algorithms, and Bayesian statistics. While many early AI programs, like IBM's Deep Blue, which defeated Garry Kasparov in chess in 1997, were rule-based and dependent on human programming, machine learning is a tool through which computers have the ability to teach themselves, and set their own rules. In 2016, Google's DeepMind beat the world champion in Go by using machine learning--training itself on a large data set of expert moves.
There are several kinds of machine learning:
- In supervised learning, the 'trainer' will present the computer with certain rules that connect an input (an object's feature, like 'smooth,' for example) with an output (the object itself, like a marble).
- In unsupervised learning, the computer is given inputs and is left alone to discover patterns.
- In reinforcement learning, a computer system receives input continuously (in the case of a driverless car receiving input about the road, for example) and constantly is improving.
A massive amount of data is required to train algorithms for machine learning. First, the 'training data' must be labeled (e.g., a GPS location attached to a photo). Then it is 'classified.' This happens when features of the object in question are labeled and put into the system with a set of rules that lead to a prediction. For example, 'red' and 'round' are inputs into the system that leads to the output: Apple. Similarly, a learning algorithm could be left alone to create its own rules that will apply when it is provided with a large set of the object--like a group of apples, and the machine figures out that they have properties like 'round' and 'red' in common.
SEE: What is machine learning? Everything you need to know (ZDNet)
Many cases of machine learning involve 'deep learning,' a subset of ML that uses algorithms that are layered, and form a network to process information and reach predictions. What distinguishes deep learning is the fact that the system can learn on its own, without human training.
Additional resources Starman tesla live stream.
- Understanding the differences between AI, machine learning, and deep learning (TechRepublic)
- Video: Is machine learning right for your business? (TechRepublic)
Microsoft says AI and machine learning driven by open source and the cloud (ZDNet)
IBM Watson: The inside story of how the Jeopardy-winning supercomputer was born, and what it wants to do next (TechRepublic cover story)
Google AI gets better at 'seeing' the world by learning what to focus on (TechRepublic)
When did machine learning become popular?
Machine learning was popular in the 1990s, and has seen a recent resurgence. Here are some timeline highlights.
- 2011: Google Brain was created, which was a deep neural network that could identify and categorize objects.
- 2014: Facebook's DeepFace algorithm was introduced. The algorithm could recognize people from a set of photos.
- 2015: Amazon launched its machine learning platform, and Microsoft offered a Distributed Machine Learning Toolkit.
- 2016: Google's DeepMind program 'AlphaGo' beat the world champion, Lee Sedol, at the complex game of Go.
- 2017: Google announced that its machine learning tools can recognize objects in photos and understand speech better than humans.
- 2018: Alphabet subsidiary Waymo launched the ML-powered self-driving ride hailing service in Phoenix, AZ.
2020: Machine learning algorithms are brought into play against the COVID-19 pandemic, helping to speed vaccine research and improve the ability to track the virus' spread.
Additional resources
- Google announces 'hum to search' machine learning music search feature (TechRepublic)
Microsoft releases preview of Lobe training app for machine-learning (ZDNet)
Alibaba neural network defeats human in global reading test (ZDNet)

Why does machine learning matter?
Aside from the tremendous power machine learning has to beat humans at games like Jeopardy, chess, and Go, machine learning has many practical applications. Machine learning tools are used to translate messages on Facebook, spot faces from photos, and find locations around the globe that have certain geographic features. IBM Watson is used to help doctors make cancer treatment decisions. Driverless cars use machine learning to gather information from the environment. Machine learning is also central to fraud prevention. Unsupervised machine learning, combined with human experts, has been proven to be very accurate in detecting cybersecurity threats, for example.
SEE: All of TechRepublic's cheat sheets and smart person's guides
While there are many potential benefits of AI, there are also concerns about its usage. Many worry that AI (like automation) will put human jobs at risk. And whether or not AI replaces humans at work, it will definitely shift the kinds of jobs that are necessary. Machine learning's requirement for labeled data, for example, has meant a huge need for humans to manually do the labeling.
As machine learning and AI in the workplace have evolved, many of its applications have centered on assisting workers rather than replacing them outright. This was especially true during the COVID-19 pandemic, which forced many companies to send large portions of their workforce home to work remotely, leading to AI bots and machine learning supplementing humans to take care of mundane tasks.
There are several institutions dedicated to exploring the impact of artificial intelligence. Here are a few (culled from our Twitter list of AI insiders).
- The Future of Life Institute brings together some of the greatest minds--from the co-founder of Skype to professors at Harvard and MIT--to explore some of the big questions about our future with machines. This Cambridge-based institute also has a stellar lineup on its scientific advisory board, from Nick Bostrom to Elon Musk to Morgan Freeman.
- The Future of Humanity Institute at Oxford is one of the premier sites for cutting-edge academic research. The FHI Twitter feed is a wonderful place for content on the latest in AI, and the many retweets by the account are also useful in finding other Twitter users who are working on the latest in artificial intelligence.
- The Machine Intelligence Research Institute at Berkeley is an excellent resource for the latest academic work in artificial intelligence. MIRI exists, according to Twitter, not only to investigate AI, but also to 'ensure that the creation of smarter-than-human intelligence has a positive impact.'
Additional resources
- IBM Watson CTO: The 3 ethical principles AI needs to embrace (TechRepublic)
- Forrester: Automation could lead to another jobless recovery (TechRepublic)
- Machine learning helps science tackle Alzheimer's (CBS News)
Which industries use machine learning?
Just about any organization that wants to capitalize on its data to gain insights, improve relationships with customers, increase sales, or be competitive at a specific task will rely on machine learning. It has applications in government, business, education--virtually anyone who wants to make predictions, and has a large enough data set, can use machine learning to achieve their goals.
SEE:Sensor'd enterprise: IoT, ML, and big data (ZDNet special report) | Download the report as a PDF (TechRepublic)
Along with analytics, machine learning can be used to supplement human workers by taking on mundane tasks and freeing them to do more meaningful, innovative, and productive work. Like with analytics, and business that has employees dealing with repetitive, high-volume tasks can benefit from machine learning.
Additional resources
- The 6 most in-demand AI jobs, and how to get them (TechRepublic)
- Cheat sheet: How to become a data scientist (TechRepublic)
- MIT's automated machine learning works 100x faster than human data scientists (TechRepublic)
- Apple, IBM add machine learning muscle to enterprise iOS pact (ZDNet)
How do businesses use machine learning?
2017 was a huge year for growth in the capabilities of machine learning, and 2018 set the stage for explosive growth that, by early 2020, found that 85% of businesses were using some form of AI in their deployed applications.
One of the things that may be holding that growth back, Deloitte said, is confusion--just what is machine learning capable of doing for businesses?
There are numerous examples of how businesses are leveraging machine learning, and all of it breaks down to the same basic thing: Processing massive amounts of data to draw conclusions much faster than a team of data scientists ever could.
Jupyter cheat sheet pdf. Some examples of business uses of machine learning include:
- Alphabet-owned security firm Chronicle is using machine learning to identify cyberthreats and minimize the damage they can cause.
- Airbus Defense & Space is using ML-based image recognition technology to decrease the error rate of cloud recognition in satellite images.
- Global Fishing Watch is fighting overfishing by monitoring the GPS coordinates of fishing vessels, which has enabled them to monitor the whole ocean at once.
- Insurance firm AXA raised accident prediction accuracy by 78% by using machine learning to build accurate driver risk profiles.
- Japanese food safety company Kewpie has automated detection of defective potato cubes so that workers don't have to spend hours watching for them.
Yelp uses deep learning to classify photos people take of businesses by certain tags.
MIT's OptiVax can develop and test peptide vaccines for COVID-19 and other diseases in a completely virtual environment with variables including geographic coverage, population data, and more.
Machine Learning Cheat Sheet Pdf
SEE: Executive's guide to AI in business (free ebook) (TechRepublic)
Any business that deals with big data analysis can use machine learning technology to speed up the process and put humans to better use, and the particulars can vary greatly from industry to industry.
AI applications don't come first--they're tools used to solve business problems, and should be seen as such. Finding the proper application for machine learning technology involves asking the right questions, or being faced with a massive wall of data that would be impossible for a human to process.
Additional resources
- 5 tips to overcome machine learning adoption barriers in the enterprise (TechRepublic)
- How the NFL and Amazon unleashed 'Next Gen Stats' to grok football games (TechRepublic)
- Robot boats from MIT can now carry passengers (TechRepublic)
- Predictive analytics: A cheat sheet (TechRepublic)
- How ML and AI will transform business intelligence and analytics (ZDNet)
- Zoom meetings: You can now add live captions to your call – and they actually work (ZDNet)
- AI and the Future of Business (ZDNet special feature)
- How to launch a successful AI startup (TechRepublic)
- The practical applications of AI: 6 videos (TechRepublic)
What are the security and ethical concerns about machine learning?
There are a number of concerns about using machine learning and AI, including the security of cloud-hosted data and the ethical considerations of self-driving cars.
From a security perspective, there are always concerns about the theft of large amounts of data, but security fears go beyond how to lock down data repositories.
Security professionals are nearly universally concerned about the potential of AI to bypass antimalware software and other security measures, and they're right to be worried: Artificial intelligence software has been developed that can modify malware to bypass AI-powered antimalware platforms.
Several tech leaders, like Elon Musk, Stephen Hawking, and Bill Gates, have expressed worries about how AI may be misused, and the importance of creating ethical AI. Evidenced by the disaster of Microsoft's racist chatbot, Tay, AI can go wrong if left unmonitored.
SEE: Machine learning as a service: Can privacy be taught? (ZDNet)
Ethical concerns abound in the machine learning world as well; one example is a self-driving vehicle adaptation of the trolley problem thought experiment. In short, when a self-driving vehicle is presented with a choice between killing its occupants or a pedestrian, which is the right choice to make? There's no clear answer with philosophical problems like this one--no matter how the machine is programmed, it has to make a moral judgement about the value of human lives.
Deep fake videos, which realistically replace one person's face and/or voice with someone else's based on photos and other recordings, have the potential to upset elections, insert unwilling people into pornography, and otherwise insert individuals into situtations they aren't okay with. The far-reaching effects of this machine learning-powered tool could be devastating.
Along with whether giving learning machines the ability to make moral decisions is correct, or whether access to certain ML tools is socially dangerous, there are issues of the other major human cost likely to come with machine learning: Job loss.
If the AI revolution is truly the next major shift in the world, there are a lot of jobs that will cease to exist, and it isn't necessarily the ones you'd think. While many low-skilled jobs are definitely at risk of being eliminated, so are jobs that require a high degree of training but are based on simple concepts like pattern recognition.
Azure Machine Learning Cheat Sheet
Radiologists, pathologists, oncologists, and other similar professions are all based on finding and diagnosing irregularities, something that machine learning is particularly suited to do.
There's also the ethical concern of barrier to entry--while machine learning software itself isn't expensive, only the largest enterprises in the world have the vast stores of data necessary to properly train learning machines to provide reliable results.

By Afshine Amidi and Shervine Amidi
Classification metrics
In a context of a binary classification, here are the main metrics that are important to track in order to assess the performance of the model.
Confusion matrix Gazette garage sales. The confusion matrix is used to have a more complete picture when assessing the performance of a model. It is defined as follows:
| Predicted class | |||
| + | - | ||
| Actual class | + | TP True Positives | FN False Negatives Type II error |
| - | FP False Positives Type I error | TN True Negatives |
Main metrics The following metrics are commonly used to assess the performance of classification models:
| Metric | Formula | Interpretation |
| Accuracy | $displaystylefrac{textrm{TP}+textrm{TN}}{textrm{TP}+textrm{TN}+textrm{FP}+textrm{FN}}$ | Overall performance of model |
| Precision | $displaystylefrac{textrm{TP}}{textrm{TP}+textrm{FP}}$ | How accurate the positive predictions are |
| Recall Sensitivity | $displaystylefrac{textrm{TP}}{textrm{TP}+textrm{FN}}$ | Coverage of actual positive sample |
| Specificity | $displaystylefrac{textrm{TN}}{textrm{TN}+textrm{FP}}$ | Coverage of actual negative sample |
| F1 score | $displaystylefrac{2textrm{TP}}{2textrm{TP}+textrm{FP}+textrm{FN}}$ | Hybrid metric useful for unbalanced classes |
ROC The receiver operating curve, also noted ROC, is the plot of TPR versus FPR by varying the threshold. These metrics are are summed up in the table below:
| Metric | Formula | Equivalent |
| True Positive Rate TPR | $displaystylefrac{textrm{TP}}{textrm{TP}+textrm{FN}}$ | Recall, sensitivity |
| False Positive Rate FPR | $displaystylefrac{textrm{FP}}{textrm{TN}+textrm{FP}}$ | 1-specificity |
AUC The area under the receiving operating curve, also noted AUC or AUROC, is the area below the ROC as shown in the following figure:
Regression metrics
Basic metrics Given a regression model $f$, the following metrics are commonly used to assess the performance of the model:
| Total sum of squares | Explained sum of squares | Residual sum of squares |
| $displaystyletextrm{SS}_{textrm{tot}}=sum_{i=1}^m(y_i-overline{y})^2$ | $displaystyletextrm{SS}_{textrm{reg}}=sum_{i=1}^m(f(x_i)-overline{y})^2$ | $displaystyletextrm{SS}_{textrm{res}}=sum_{i=1}^m(y_i-f(x_i))^2$ |
Coefficient of determination The coefficient of determination, often noted $R^2$ or $r^2$, provides a measure of how well the observed outcomes are replicated by the model and is defined as follows:
[boxed{R^2=1-frac{textrm{SS}_textrm{res}}{textrm{SS}_textrm{tot}}}]Main metrics The following metrics are commonly used to assess the performance of regression models, by taking into account the number of variables $n$ that they take into consideration:
| Mallow's Cp | AIC | BIC | Adjusted $R^2$ |
| $displaystylefrac{textrm{SS}_{textrm{res}}+2(n+1)widehat{sigma}^2}{m}$ | $displaystyle2Big[(n+2)-log(L)Big]$ | $displaystylelog(m)(n+2)-2log(L)$ | $displaystyle1-frac{(1-R^2)(m-1)}{m-n-1}$ |
where $L$ is the likelihood and $widehat{sigma}^2$ is an estimate of the variance associated with each response.
Model selection
Vocabulary When selecting a model, we distinguish 3 different parts of the data that we have as follows:
| Training set | Validation set | Testing set |
| • Model is trained • Usually 80% of the dataset | • Model is assessed • Usually 20% of the dataset • Also called hold-out or development set | • Model gives predictions • Unseen data |
Once the model has been chosen, it is trained on the entire dataset and tested on the unseen test set. These are represented in the figure below:
Cross-validation Cross-validation, also noted CV, is a method that is used to select a model that does not rely too much on the initial training set. The different types are summed up in the table below:
| k-fold | Leave-p-out |
| • Training on $k-1$ folds and assessment on the remaining one • Generally $k=5$ or $10$ | • Training on $n-p$ observations and assessment on the $p$ remaining ones • Case $p=1$ is called leave-one-out |
The most commonly used method is called $k$-fold cross-validation and splits the training data into $k$ folds to validate the model on one fold while training the model on the $k-1$ other folds, all of this $k$ times. The error is then averaged over the $k$ folds and is named cross-validation error.
Regularization The regularization procedure aims at avoiding the model to overfit the data and thus deals with high variance issues. The following table sums up the different types of commonly used regularization techniques:
| LASSO | Ridge | Elastic Net |
| • Shrinks coefficients to 0 • Good for variable selection | Makes coefficients smaller | Tradeoff between variable selection and small coefficients |
| $..+lambda||theta||_1$ $lambdainmathbb{R}$ | $..+lambda||theta||_2^2$ $lambdainmathbb{R}$ | $..+lambdaBig[(1-alpha)||theta||_1+alpha||theta||_2^2Big]$ $lambdainmathbb{R},alphain[0,1]$ |
Diagnostics
Bias The bias of a model is the difference between the expected prediction and the correct model that we try to predict for given data points.
Variance The variance of a model is the variability of the model prediction for given data points.
Bias/variance tradeoff The simpler the model, the higher the bias, and the more complex the model, the higher the variance.
| Underfitting | Just right | Overfitting | |
| Symptoms | • High training error • Training error close to test error • High bias | • Training error slightly lower than test error | • Very low training error • Training error much lower than test error • High variance |
| Regression illustration | |||
| Classification illustration | |||
| Deep learning illustration | |||
| Possible remedies | • Complexify model • Add more features • Train longer | • Perform regularization • Get more data |
Error analysis Error analysis is analyzing the root cause of the difference in performance between the current and the perfect models.
Ablative analysis Ablative analysis is analyzing the root cause of the difference in performance between the current and the baseline models.
© TechRepublic Machine learning: A cheat sheet
Artificial intelligence (AI), which has been around since the 1950s, has seen ebbs and flows in popularity over the last 60+ years. But today, with the recent explosion of big data, high-powered parallel processing, and advanced neural algorithms, we are seeing a renaissance in AI--and companies from Amazon to Facebook to Google are scrambling to take the lead. According to AI expert Roman Yampolskiy, 2016 was the year of 'AI on steroids,' and its explosive growth hasn't stopped.
While there are different forms of AI, machine learning (ML) represents today's most widely valued mechanism for reaching intelligence. Here's what it means.
SEE: Managing AI and ML in the enterprise (ZDNet special report) | Download the report as a PDF (TechRepublic)
Executive summary
- What is machine learning? Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence. Instead of relying on explicit programming, it is a system through which computers use a massive set of data and apply algorithms to 'train' on--to teach themselves--and make predictions.
- When did machine learning become popular? The term 'artificial intelligence' was coined in the 1950s by Alan Turing. Machine learning became popular in the 1990s, and returned to the public eye when Google's DeepMind beat the world champion of Go in 2016. Since then, ML applications and machine learning's popularity have only increased.
- Why does machine learning matter? Machine learning systems are able to quickly apply knowledge and training from large data sets to excel at facial recognition, speech recognition, object recognition, translation, and many other tasks.
- Which industries use machine learning? Machine learning touches industries spanning from government to education to healthcare. It can be used by businesses focused on marketing, social media, customer service, driverless cars, and many more. It is now widely regarded as a core tool for decision making.
- How do businesses use machine learning? Business applications of machine learning are numerous, but all boil down to one type of use: Processing, sorting, and finding patterns in huge amounts of data that would be impractical for humans to make sense of.
- What are the security and ethical concerns about machine learning? AI has already been trained to bypass advanced antimalware software, and it has the potential to be a huge security risk in the future. Ethical concerns also abound, especially in relation to the loss of jobs and the practicality of allowing machines to make moral decisions like those that would be necessary in self-driving vehicles.
- What machine learning tools are available? Businesses like IBM, Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and others offer tools for machine learning. There are free platforms as well.
SEE: Managing AI and ML in the enterprise 2020: Tech leaders increase project development and implementation (TechRepublic Premium)
What is machine learning?
Machine learning is a branch of AI. Other tools for reaching AI include rule-based engines, evolutionary algorithms, and Bayesian statistics. While many early AI programs, like IBM's Deep Blue, which defeated Garry Kasparov in chess in 1997, were rule-based and dependent on human programming, machine learning is a tool through which computers have the ability to teach themselves, and set their own rules. In 2016, Google's DeepMind beat the world champion in Go by using machine learning--training itself on a large data set of expert moves.
There are several kinds of machine learning:
- In supervised learning, the 'trainer' will present the computer with certain rules that connect an input (an object's feature, like 'smooth,' for example) with an output (the object itself, like a marble).
- In unsupervised learning, the computer is given inputs and is left alone to discover patterns.
- In reinforcement learning, a computer system receives input continuously (in the case of a driverless car receiving input about the road, for example) and constantly is improving.
A massive amount of data is required to train algorithms for machine learning. First, the 'training data' must be labeled (e.g., a GPS location attached to a photo). Then it is 'classified.' This happens when features of the object in question are labeled and put into the system with a set of rules that lead to a prediction. For example, 'red' and 'round' are inputs into the system that leads to the output: Apple. Similarly, a learning algorithm could be left alone to create its own rules that will apply when it is provided with a large set of the object--like a group of apples, and the machine figures out that they have properties like 'round' and 'red' in common.
SEE: What is machine learning? Everything you need to know (ZDNet)
Many cases of machine learning involve 'deep learning,' a subset of ML that uses algorithms that are layered, and form a network to process information and reach predictions. What distinguishes deep learning is the fact that the system can learn on its own, without human training.
Additional resources Starman tesla live stream.
- Understanding the differences between AI, machine learning, and deep learning (TechRepublic)
- Video: Is machine learning right for your business? (TechRepublic)
Microsoft says AI and machine learning driven by open source and the cloud (ZDNet)
IBM Watson: The inside story of how the Jeopardy-winning supercomputer was born, and what it wants to do next (TechRepublic cover story)
Google AI gets better at 'seeing' the world by learning what to focus on (TechRepublic)
When did machine learning become popular?
Machine learning was popular in the 1990s, and has seen a recent resurgence. Here are some timeline highlights.
- 2011: Google Brain was created, which was a deep neural network that could identify and categorize objects.
- 2014: Facebook's DeepFace algorithm was introduced. The algorithm could recognize people from a set of photos.
- 2015: Amazon launched its machine learning platform, and Microsoft offered a Distributed Machine Learning Toolkit.
- 2016: Google's DeepMind program 'AlphaGo' beat the world champion, Lee Sedol, at the complex game of Go.
- 2017: Google announced that its machine learning tools can recognize objects in photos and understand speech better than humans.
- 2018: Alphabet subsidiary Waymo launched the ML-powered self-driving ride hailing service in Phoenix, AZ.
2020: Machine learning algorithms are brought into play against the COVID-19 pandemic, helping to speed vaccine research and improve the ability to track the virus' spread.
Additional resources
- Google announces 'hum to search' machine learning music search feature (TechRepublic)
Microsoft releases preview of Lobe training app for machine-learning (ZDNet)
Alibaba neural network defeats human in global reading test (ZDNet)
Why does machine learning matter?
Aside from the tremendous power machine learning has to beat humans at games like Jeopardy, chess, and Go, machine learning has many practical applications. Machine learning tools are used to translate messages on Facebook, spot faces from photos, and find locations around the globe that have certain geographic features. IBM Watson is used to help doctors make cancer treatment decisions. Driverless cars use machine learning to gather information from the environment. Machine learning is also central to fraud prevention. Unsupervised machine learning, combined with human experts, has been proven to be very accurate in detecting cybersecurity threats, for example.
SEE: All of TechRepublic's cheat sheets and smart person's guides
While there are many potential benefits of AI, there are also concerns about its usage. Many worry that AI (like automation) will put human jobs at risk. And whether or not AI replaces humans at work, it will definitely shift the kinds of jobs that are necessary. Machine learning's requirement for labeled data, for example, has meant a huge need for humans to manually do the labeling.
As machine learning and AI in the workplace have evolved, many of its applications have centered on assisting workers rather than replacing them outright. This was especially true during the COVID-19 pandemic, which forced many companies to send large portions of their workforce home to work remotely, leading to AI bots and machine learning supplementing humans to take care of mundane tasks.
There are several institutions dedicated to exploring the impact of artificial intelligence. Here are a few (culled from our Twitter list of AI insiders).
- The Future of Life Institute brings together some of the greatest minds--from the co-founder of Skype to professors at Harvard and MIT--to explore some of the big questions about our future with machines. This Cambridge-based institute also has a stellar lineup on its scientific advisory board, from Nick Bostrom to Elon Musk to Morgan Freeman.
- The Future of Humanity Institute at Oxford is one of the premier sites for cutting-edge academic research. The FHI Twitter feed is a wonderful place for content on the latest in AI, and the many retweets by the account are also useful in finding other Twitter users who are working on the latest in artificial intelligence.
- The Machine Intelligence Research Institute at Berkeley is an excellent resource for the latest academic work in artificial intelligence. MIRI exists, according to Twitter, not only to investigate AI, but also to 'ensure that the creation of smarter-than-human intelligence has a positive impact.'
Additional resources
- IBM Watson CTO: The 3 ethical principles AI needs to embrace (TechRepublic)
- Forrester: Automation could lead to another jobless recovery (TechRepublic)
- Machine learning helps science tackle Alzheimer's (CBS News)
Which industries use machine learning?
Just about any organization that wants to capitalize on its data to gain insights, improve relationships with customers, increase sales, or be competitive at a specific task will rely on machine learning. It has applications in government, business, education--virtually anyone who wants to make predictions, and has a large enough data set, can use machine learning to achieve their goals.
SEE:Sensor'd enterprise: IoT, ML, and big data (ZDNet special report) | Download the report as a PDF (TechRepublic)
Along with analytics, machine learning can be used to supplement human workers by taking on mundane tasks and freeing them to do more meaningful, innovative, and productive work. Like with analytics, and business that has employees dealing with repetitive, high-volume tasks can benefit from machine learning.
Additional resources
- The 6 most in-demand AI jobs, and how to get them (TechRepublic)
- Cheat sheet: How to become a data scientist (TechRepublic)
- MIT's automated machine learning works 100x faster than human data scientists (TechRepublic)
- Apple, IBM add machine learning muscle to enterprise iOS pact (ZDNet)
How do businesses use machine learning?
2017 was a huge year for growth in the capabilities of machine learning, and 2018 set the stage for explosive growth that, by early 2020, found that 85% of businesses were using some form of AI in their deployed applications.
One of the things that may be holding that growth back, Deloitte said, is confusion--just what is machine learning capable of doing for businesses?
There are numerous examples of how businesses are leveraging machine learning, and all of it breaks down to the same basic thing: Processing massive amounts of data to draw conclusions much faster than a team of data scientists ever could.
Jupyter cheat sheet pdf. Some examples of business uses of machine learning include:
- Alphabet-owned security firm Chronicle is using machine learning to identify cyberthreats and minimize the damage they can cause.
- Airbus Defense & Space is using ML-based image recognition technology to decrease the error rate of cloud recognition in satellite images.
- Global Fishing Watch is fighting overfishing by monitoring the GPS coordinates of fishing vessels, which has enabled them to monitor the whole ocean at once.
- Insurance firm AXA raised accident prediction accuracy by 78% by using machine learning to build accurate driver risk profiles.
- Japanese food safety company Kewpie has automated detection of defective potato cubes so that workers don't have to spend hours watching for them.
Yelp uses deep learning to classify photos people take of businesses by certain tags.
MIT's OptiVax can develop and test peptide vaccines for COVID-19 and other diseases in a completely virtual environment with variables including geographic coverage, population data, and more.
Machine Learning Cheat Sheet Pdf
SEE: Executive's guide to AI in business (free ebook) (TechRepublic)
Any business that deals with big data analysis can use machine learning technology to speed up the process and put humans to better use, and the particulars can vary greatly from industry to industry.
AI applications don't come first--they're tools used to solve business problems, and should be seen as such. Finding the proper application for machine learning technology involves asking the right questions, or being faced with a massive wall of data that would be impossible for a human to process.
Additional resources
- 5 tips to overcome machine learning adoption barriers in the enterprise (TechRepublic)
- How the NFL and Amazon unleashed 'Next Gen Stats' to grok football games (TechRepublic)
- Robot boats from MIT can now carry passengers (TechRepublic)
- Predictive analytics: A cheat sheet (TechRepublic)
- How ML and AI will transform business intelligence and analytics (ZDNet)
- Zoom meetings: You can now add live captions to your call – and they actually work (ZDNet)
- AI and the Future of Business (ZDNet special feature)
- How to launch a successful AI startup (TechRepublic)
- The practical applications of AI: 6 videos (TechRepublic)
What are the security and ethical concerns about machine learning?
There are a number of concerns about using machine learning and AI, including the security of cloud-hosted data and the ethical considerations of self-driving cars.
From a security perspective, there are always concerns about the theft of large amounts of data, but security fears go beyond how to lock down data repositories.
Security professionals are nearly universally concerned about the potential of AI to bypass antimalware software and other security measures, and they're right to be worried: Artificial intelligence software has been developed that can modify malware to bypass AI-powered antimalware platforms.
Several tech leaders, like Elon Musk, Stephen Hawking, and Bill Gates, have expressed worries about how AI may be misused, and the importance of creating ethical AI. Evidenced by the disaster of Microsoft's racist chatbot, Tay, AI can go wrong if left unmonitored.
SEE: Machine learning as a service: Can privacy be taught? (ZDNet)
Ethical concerns abound in the machine learning world as well; one example is a self-driving vehicle adaptation of the trolley problem thought experiment. In short, when a self-driving vehicle is presented with a choice between killing its occupants or a pedestrian, which is the right choice to make? There's no clear answer with philosophical problems like this one--no matter how the machine is programmed, it has to make a moral judgement about the value of human lives.
Deep fake videos, which realistically replace one person's face and/or voice with someone else's based on photos and other recordings, have the potential to upset elections, insert unwilling people into pornography, and otherwise insert individuals into situtations they aren't okay with. The far-reaching effects of this machine learning-powered tool could be devastating.
Along with whether giving learning machines the ability to make moral decisions is correct, or whether access to certain ML tools is socially dangerous, there are issues of the other major human cost likely to come with machine learning: Job loss.
If the AI revolution is truly the next major shift in the world, there are a lot of jobs that will cease to exist, and it isn't necessarily the ones you'd think. While many low-skilled jobs are definitely at risk of being eliminated, so are jobs that require a high degree of training but are based on simple concepts like pattern recognition.
Azure Machine Learning Cheat Sheet
Radiologists, pathologists, oncologists, and other similar professions are all based on finding and diagnosing irregularities, something that machine learning is particularly suited to do.
There's also the ethical concern of barrier to entry--while machine learning software itself isn't expensive, only the largest enterprises in the world have the vast stores of data necessary to properly train learning machines to provide reliable results.
As time goes on, some experts predict that it's going to become more difficult for smaller firms to make an impact, making machine learning primarily a game for the largest, wealthiest companies.
Additional resources
- Why AI bias could be a good thing (TechRepublic)
- Google AI executive sees a world of trillions of devices untethered from human care (ZDNet)
- AI and ethics: One-third of executives are not aware of potential AI bias (TechRepublic)
- Artificial data reduces privacy concerns and helps with big data analysis (TechRepublic)
- Can AI really be ethical and unbiased? (ZDNet)
- 3 ways criminals use artificial intelligence in cybersecurity attacks (TechRepublic)
- Artificial Intelligence: Legal, ethical, and policy issues (ZDNet)
What machine learning tools are available?
There are many online resources about machine learning. To get an overview of how to create a machine learning system, check out this series of YouTube videos by Google Developer. There are also classes on machine learning from Coursera and many other institutions.
And to integrate machine learning into your organization, you can use resources like Microsoft's Azure, Google Cloud Machine Learning, Amazon Machine Learning, IBM Watson, and free platforms like Scikit.
Additional resources
- Amazon unveils dozens of machine learning tools (TechRepublic)
- Microsoft offers developers pre-built machine learning models for Windows 10 apps (TechRepublic)
- Cloud AutoML: How Google aims to simplify the grunt work behind AI and machine learning models (ZDNet)
- Amazon AI: Cheat sheet (TechRepublic)
- AI investment increased during the pandemic, and many business plan to do more, Gartner found (TechRepublic)
- Facebook's machine learning director shares tips for building a successful AI platform (TechRepublic)
- AI helpers aren't just for Facebook's Zuckerberg: Here's how to build your own (TechRepublic)
- How developers can take advantage of machine learning on Google Cloud Platform (TechRepublic)
- How to prepare your business to benefit from AI (TechRepublic)
Editor's note: This article was updated by Brandon Vigliarolo.
